Drawings are amounts taken out of the business by the business owner. In other words, all assets initially come from liabilities and owners’ contributions. Receivables arise when a company provides a service or sells a product to someone on credit.
Purchase of Equipment in Cash
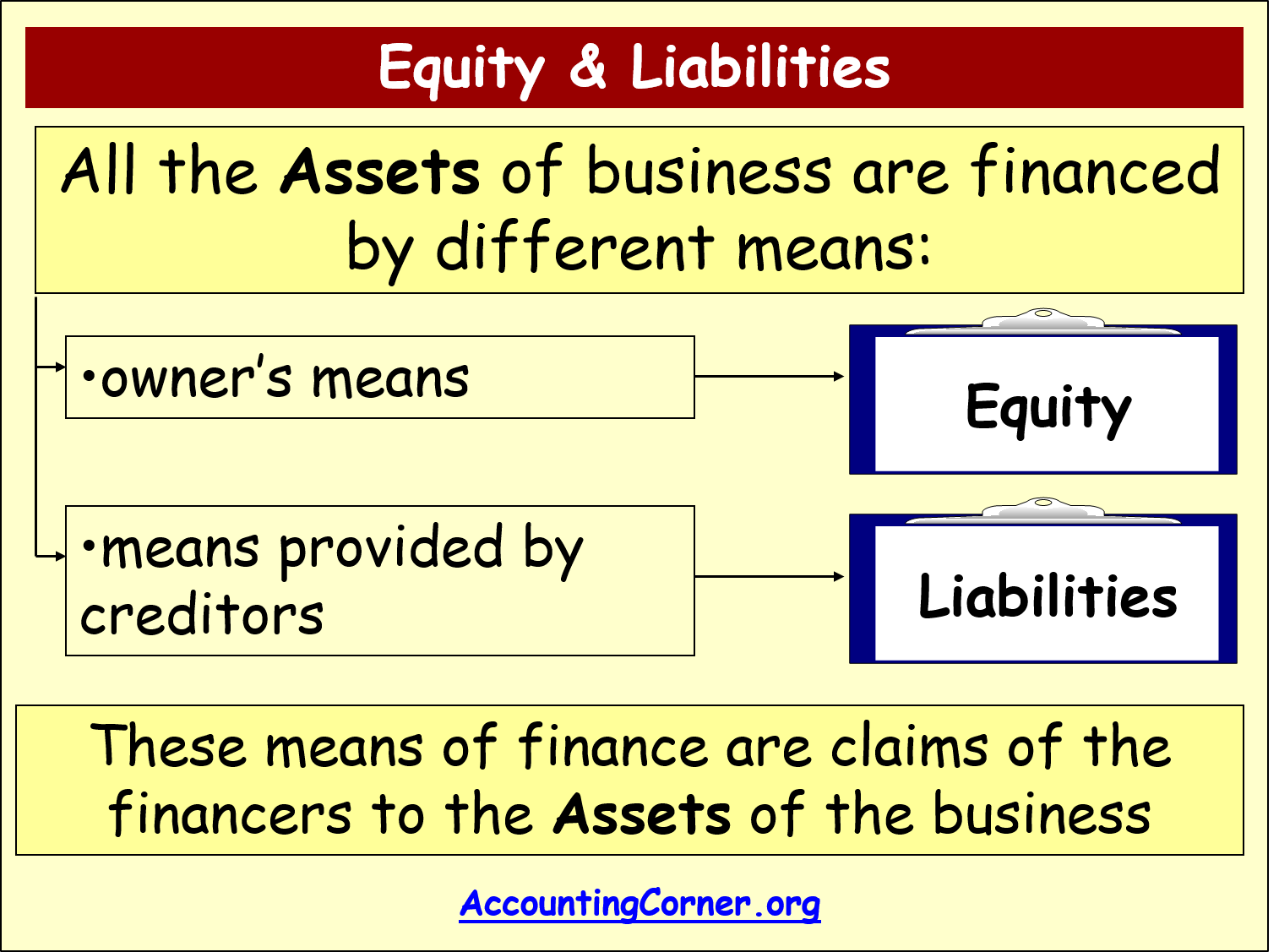
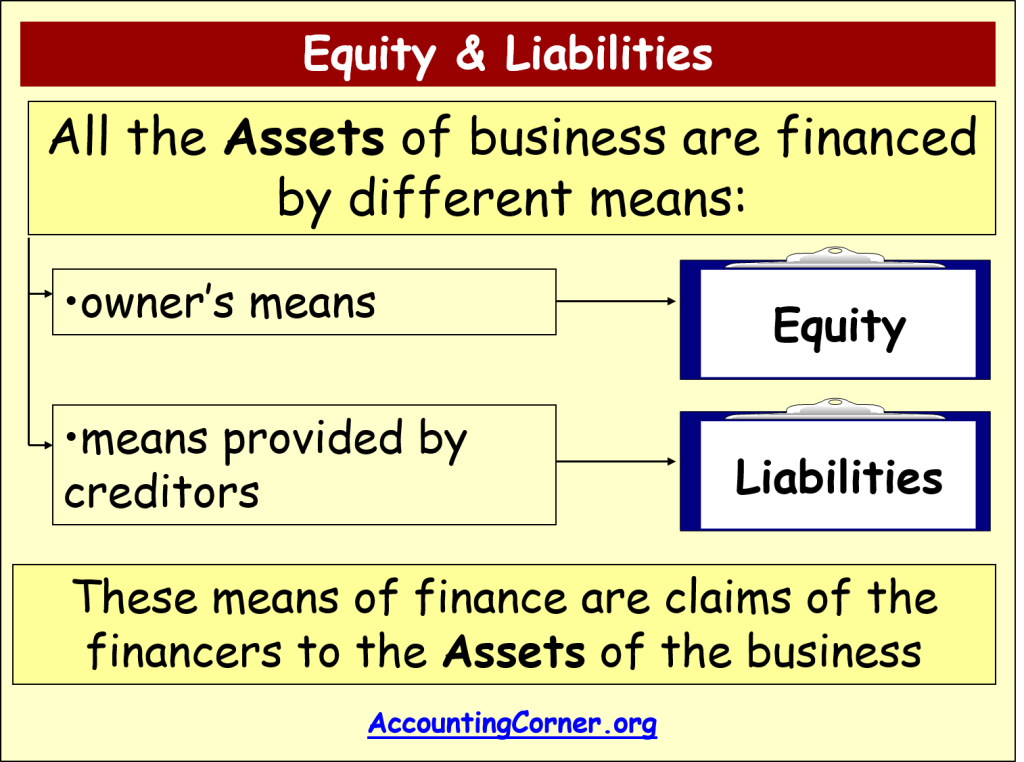
The fundamental components of the accounting equation include the calculation of both company holdings and company debts; thus, it allows owners to gauge the total value of a firm’s assets. Although the balance sheet always balances out, the accounting equation can’t tell investors how well a company is performing. Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company, while liabilities represent its obligations.
- Likewise, revenues increase equity while expenses decrease equity.
- A company’s quarterly and annual reports are basically derived directly from the accounting equations used in bookkeeping practices.
- This is how the accounting equation of Laura’s business looks like after incorporating the effects of all transactions at the end of month 1.
- To learn more about the balance sheet, see our Balance Sheet Outline.
- Using Apple’s 2023 earnings report, we can find all the information we need for the accounting equation.
- This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends.
What is your current financial priority?
Since Speakers, Inc. doesn’t have $500,000 in cash to pay for a building, it must take out a loan. Speakers, Inc. purchases a $500,000 building by paying $100,000 in cash and taking out a $400,000 outsource plug careers and employment mortgage. This business transaction decreases assets by the $100,000 of cash disbursed, increases assets by the new $500,000 building, and increases liabilities by the new $400,000 mortgage.
4: The Basic Accounting Equation
They include items such as land, buildings, equipment, and accounts receivable. This long-form equation is called the expanded accounting equation. On the other hand, equity refers to shareholder’s or owner’s equity, which is how much the shareholder or owner has staked into the company. Small business owners typically have a 100% stake in their company, while growing businesses may have an investor and share 20%.
What is The Accounting Equation in its Expanded Form?
To learn more about the income statement, see Income Statement Outline. Accounts receivable list the amounts of money owed to the company by its customers for the sale of its products. Assets include cash and cash equivalents or liquid assets, which may include Treasury bills and certificates of deposit (CDs). Typical examples of Current Liabilities include Accounts Payable (aka Trade Payables, Creditors) and bank overdrafts. Buildings, vehicles, computers, for instance, are all examples of tangible assets. Net worth in this context refers exclusively to the “book value”, i.e. how much it’s worth in accounting terms, not economic terms.
At the same time, Capital increased due to the owner’s contribution. Remember that capital is increased by contribution of owners and income, and is decreased by withdrawals and expenses. As business transactions take place, the values of the accounting elements change. A liability, in its simplest terms, is an amount of money owed to another person or organization.
Finally, a corporation is a very common entity form, with its ownership interest being represented by divisible units of ownership called shares of stock. Corporate shares are easily transferable, with the current holder(s) of the stock being the owners. Earnings give rise to increases in retained earnings, while dividends (and losses) cause decreases. The accounting equation is the backbone of the accounting and reporting system. It is central to understanding a key financial statement known as the balance sheet (sometimes called the statement of financial position).
This basic accounting equation is akin to / identical to the Balance Sheet (aka Statement of Financial Position). In worst-case scenarios, the company could go bankrupt as a result of mishandling finances using inaccurate numbers due to an unbalanced equation. To illustrate how the accounting equation works, let us analyze the transactions of a fictitious corporation, First Shop, Inc.
This statement reflects profits and losses that are themselves determined by the calculations that make up the basic accounting equation. In other words, this equation allows businesses to determine revenue as well as prepare a statement of retained earnings. This then allows them to predict future profit trends and adjust business practices accordingly.
The accounting equation states that the amount of assets must be equal to liabilities plus shareholder or owner equity. Ted is an entrepreneur who wants to start a company selling speakers for car stereo systems. After saving up money for a year, Ted decides it is time to officially start his business. He forms Speakers, Inc. and contributes $100,000 to the company in exchange for all of its newly issued shares. This business transaction increases company cash and increases equity by the same amount.
In this sense, the liabilities are considered more current than the equity. This is consistent with financial reporting where current assets and liabilities are always reported before long-term assets and liabilities. Under the accrual basis of accounting, expenses are matched with revenues on the income statement when the expenses expire or title has transferred to the buyer, rather than at the time when expenses are paid. The accounting method under which revenues are recognized on the income statement when they are earned (rather than when the cash is received). The fundamental accounting equation, also called the balance sheet equation, is the foundation for the double-entry bookkeeping system and the cornerstone of accounting science.
